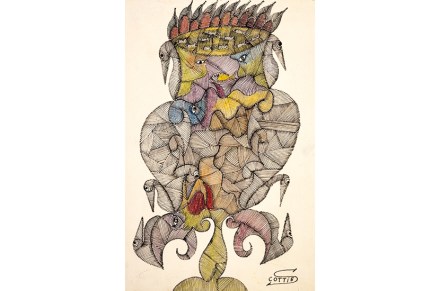
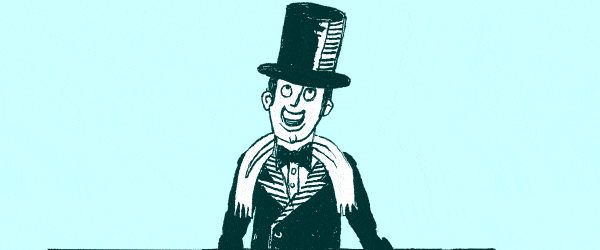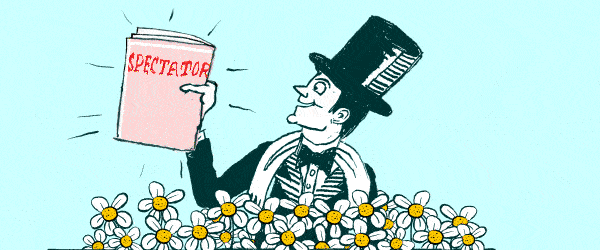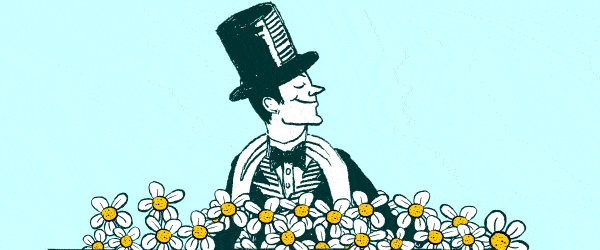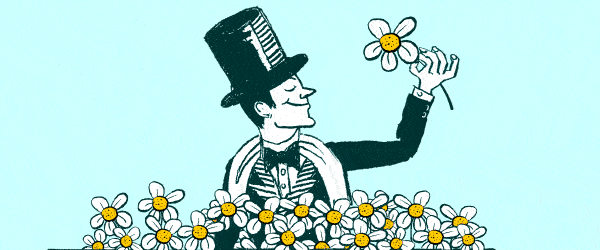
The bizarre art of Scottie Wilson deserves to be better known
On eBay I have an alert set for ‘Scottie Wilson’. Nine times out of ten, it’s a diamanté Scottie dog from the jewellers Butler & Wilson. Once in a while, it’s a gem. Scottie Wilson didn’t think much of journalists. Art critics were ‘just jugglers — dodgers’. The sort of people who went to art shows — his or anybody else’s — could be counted on to go about ‘blabbing a lot of stupid muck. A lot of blah blah. They get paid for it too!’ Which makes it tricky to write about Scottie (always Scottie, never Wilson). You just know he’d light a cigarette and scowl. I came late