The art of sexual innuendo
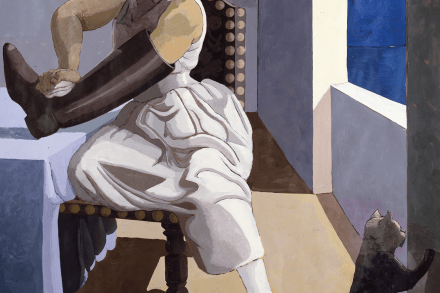
Paula Rego’s 2021 retrospective at Tate Britain demonstrated that, among art critics, ambiguity is still highly prized as a measure of merit. Martin Gayford: ‘No one, including its creator, can be aware of everything that’s going on.’ Laura Cumming at least gave examples. Of ‘The Cadet and his Sister’ (1988), she commented: ‘Bondage – physical, emotional, familial – is always in the air.’ The adjectives in that nervous parenthesis are insurance, the critic spreading her bets. The picture shows an older, bigger sister, formally dressed, with her cadet brother in uniform, wearing white ceremonial gloves. Behind them, a careful vista of trees. The painting depicts a milieu of public formality.