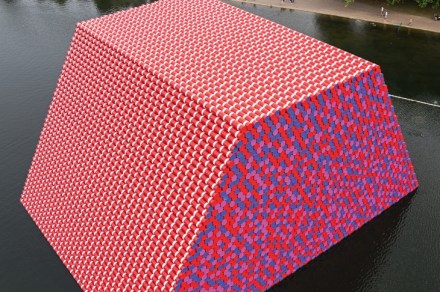
Paris’s glittering new museums
How do you manage a dictatorship? By producing ‘a succession of miracles’, according to Louis-Napoléon, that ‘dazzle and astonish’. In 1852 he inaugurated his Second Empire regime with a strategy of soft power predicated on the assumption that the loyalty of politically volatile Paris was to be won not by violent repression but by visible magnificence and grand designs. This wasn’t an original idea: it followed the policies of le Roi Soleil and Bonaparte, not to mention the Roman emperors. It worked again for Louis-Napoléon because, as well as such jaw-dropping follies as Charles Garnier’s extravagant opera house, it extended to Haussmann’s lavish investment in socially useful boulevards, sewers, housing