Osborne’s inflationary problem
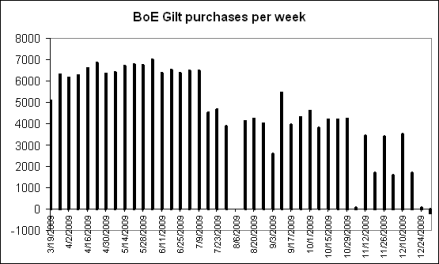
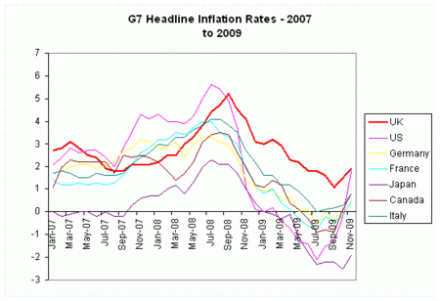
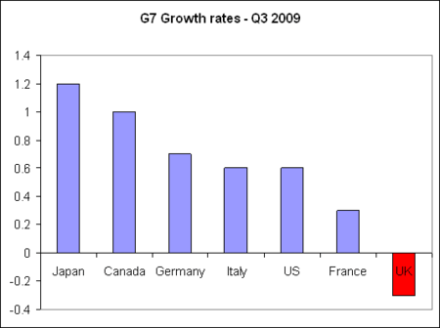
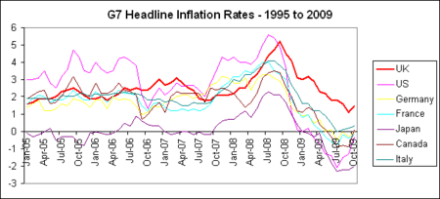
Only a week into his new job, and George Osborne has already had to exchange letters with Mervyn King about inflation. And here’s why: the CPI index hit 3.7 percent in April, up from 3.4 percent in March. Which is worrying enough when looked at in isolation – but when put alongside headline rates from other countries, it becomes damning. In China, it’s 2.8 percent. In France, 1.9 percent. In Germany, 1 percent. In the Eurozone as a whole, 1.5 percent. And in the US, 2.3 percent (for March, with the latest figures out tomorrow). Indeed, thanks in part to quantitative easing and the removal of the VAT cut, inflation