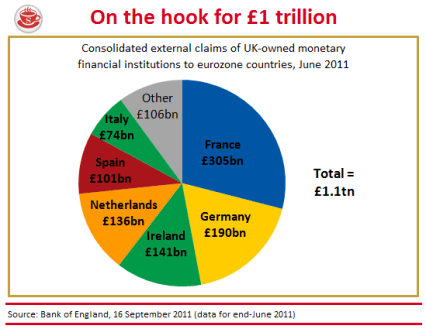
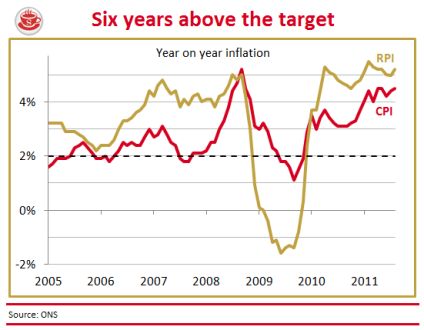
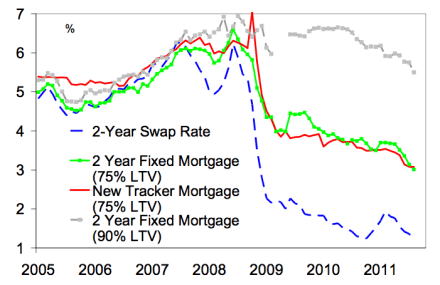
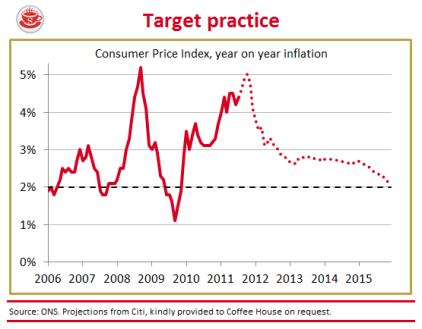
Inflation at 4.2 per cent is nothing to cheer
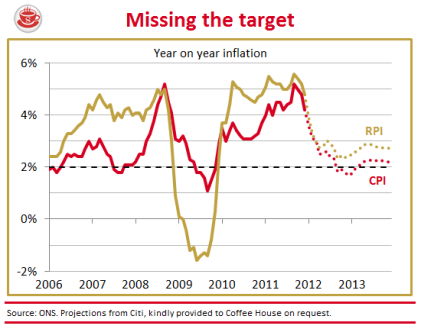
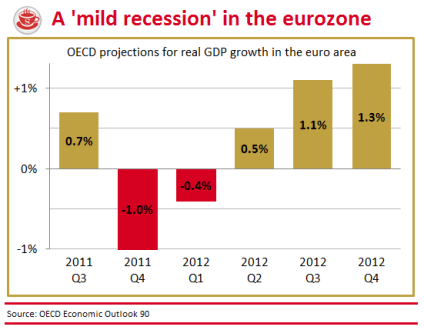
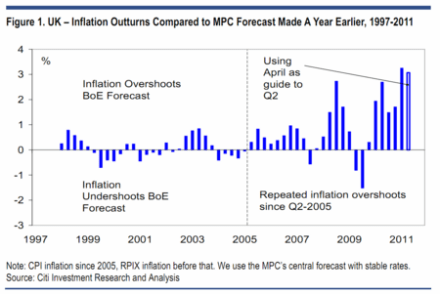
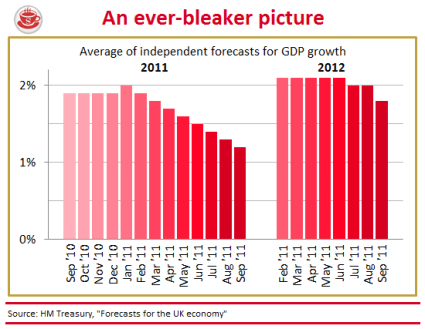
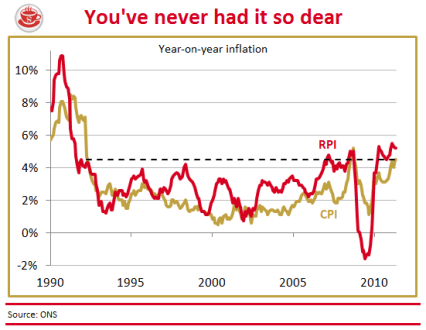
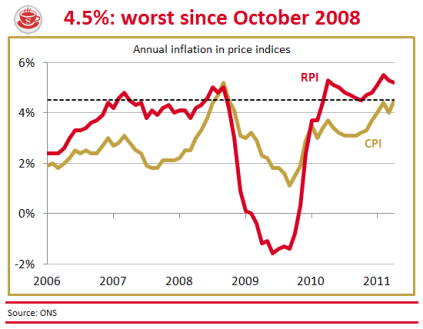
Are today’s inflation figures cause for celebration? The Consumer Price Index rose a mere 4.2 per cent in the year to December, down from 4.8 per cent in November. So, yes, a sharp drop — but only a statistical boffin could describe this as good news. Sure, a similar drop can be expected when the VAT rise drops out of the comparison figures next month. But the prices confronting British shoppers are still rising at twice the supposed inflation target, and will keep rising above this target for months to come. The following graph shows the trajectory we can expect for CPI and RPI over the next few years: The